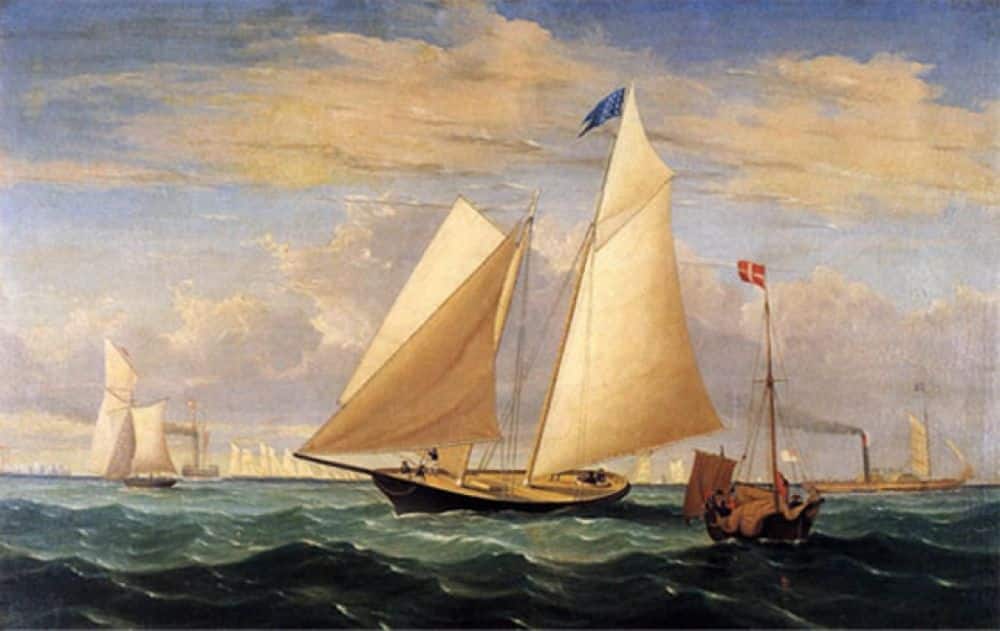
In 1851, the schooner America of New York Yacht Club sailed against 15 yachts of the Royal Yacht Squadron in the club’s annual regatta around the Isle of Wight. America finished 8 minutes ahead of the closest rival, securing victory, and beginning what would become one of the longest running competition in sports. in 1857, the Deed of Gift officially donated the America’s Cup to New York Yacht Club ensuring that it be held as a perpetual challenge trophy to promote friendly competition among nations.
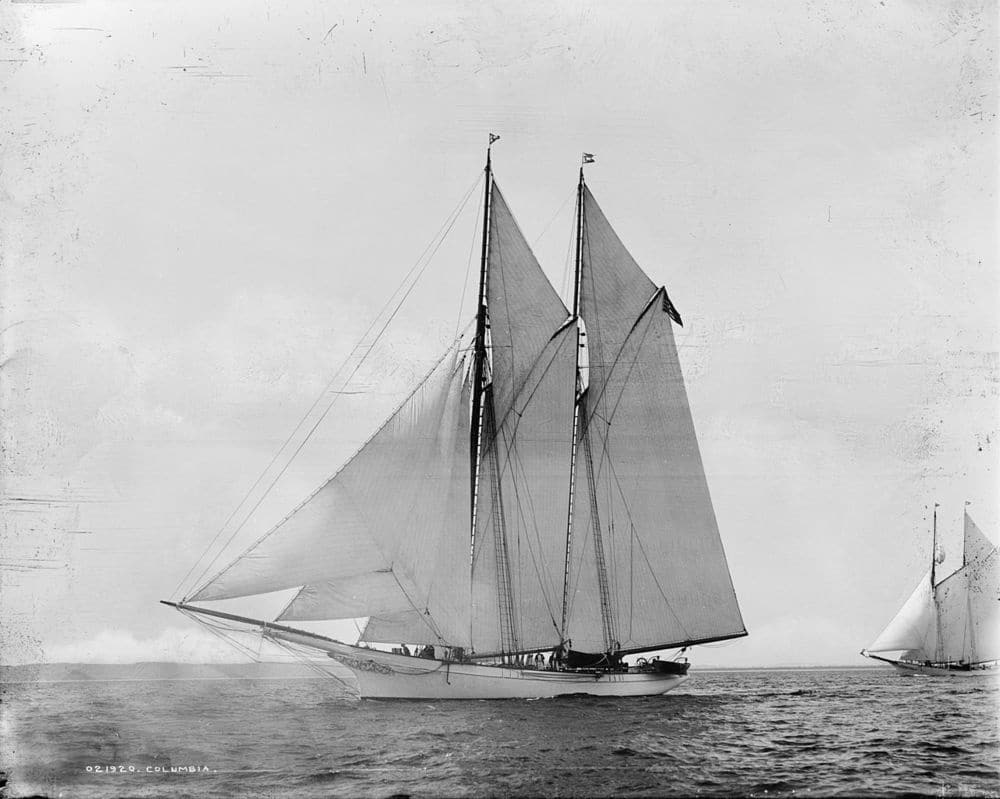

In 1871, the first official challenge to the America’s Cup came from James Lloyd Ashbury, who had previously beaten the schooner America and was emboldened by his victory. The New York Yacht Club accepted, and the schooner Columbia was chosen to defend, successfully taking the first two races before dismasting. The yacht Sappho was chosen as a replacement and continued to hold off the British challenge in the third and fourth races.
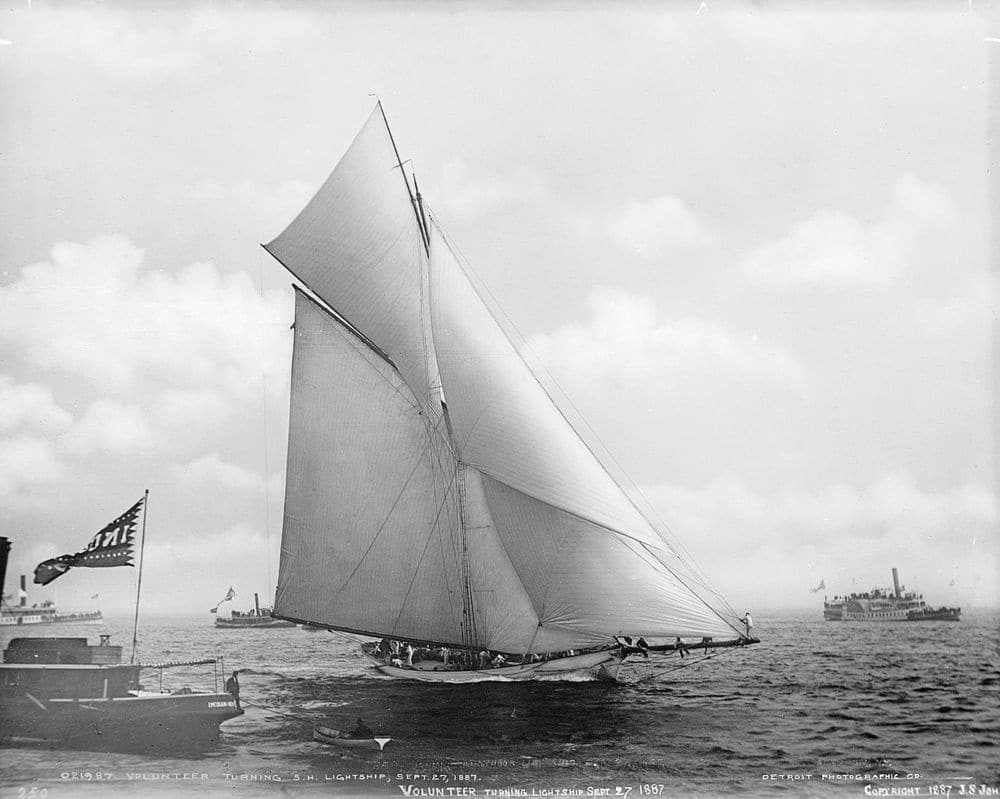

A new rule governing the design of America’s Cup yachts was drafted in 1885 after a series of Canadian challenges. Irish designer John Webb sent two yachts New York in 1885 and again in 1886 but neither could best the American designs. The final challenge under the New York Yacht Club Rule came in 1887, when Volunteer defended the Cup against the Scottish designed Thistle.
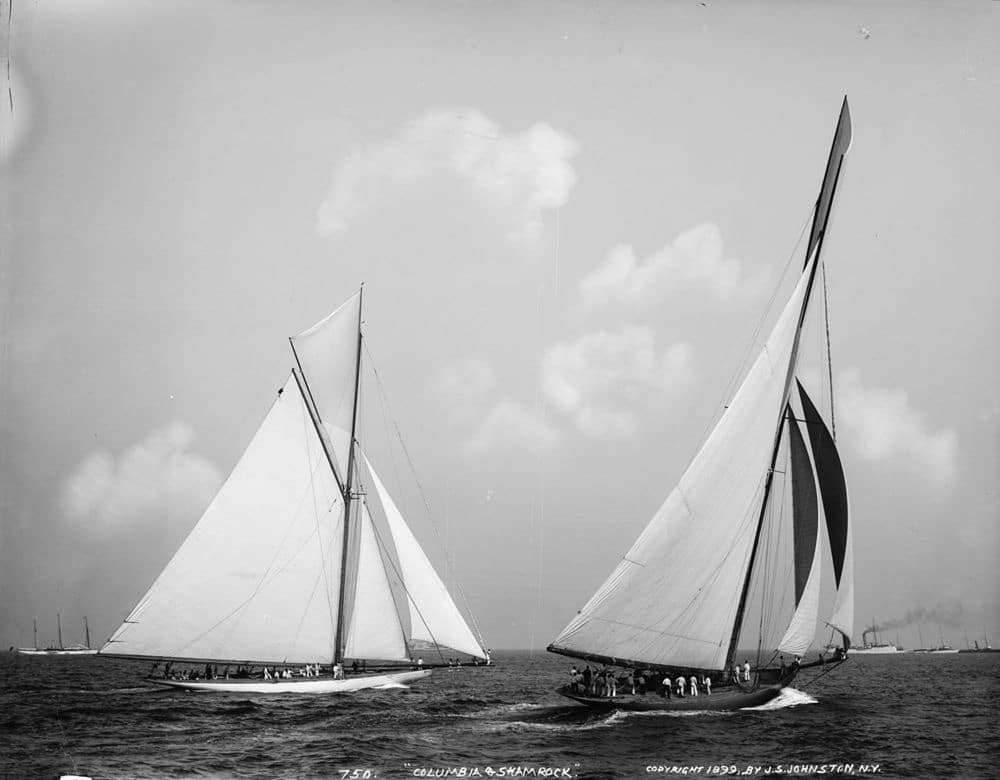

In 1889, the New York Yacht Club adopted the Seawanhaka Rating Rule. Over the next several years, Herreshoff designed boats would reign supreme, with Nathanael himself helming Vigilant to victory in 1893. In 1899, Sir James Lipton of Scotland posed the first of a series, racing Shamrock (right) against the already proven Columbia. Columbia, helmed by Charlie Barr, sailed to victory over Lipton, becoming the first yacht to defend the Cup more than once.
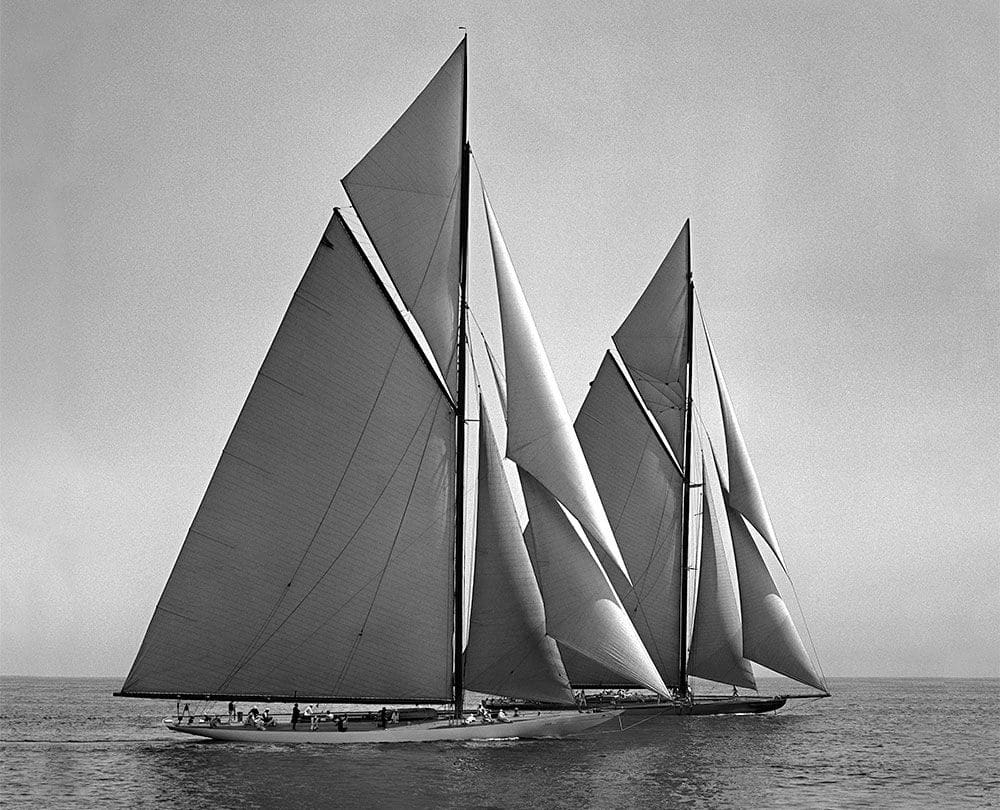

As Cup selection trials were underway for the 1914 challenge, war broke out and the Cup was cancelled, putting the first test of the newly implemented Universal Rule on hold. In 1920, the challenge resumed, with Lipton once again attempting to dethrone the Americans, this time with Shamrock IV. Lipton came the closest anyone had thus far in the event’s history to winning back the cup, winning the first two races, but the Herreshoff designed Resolute staged a comeback and went on to defend the cup for the Americans yet again.
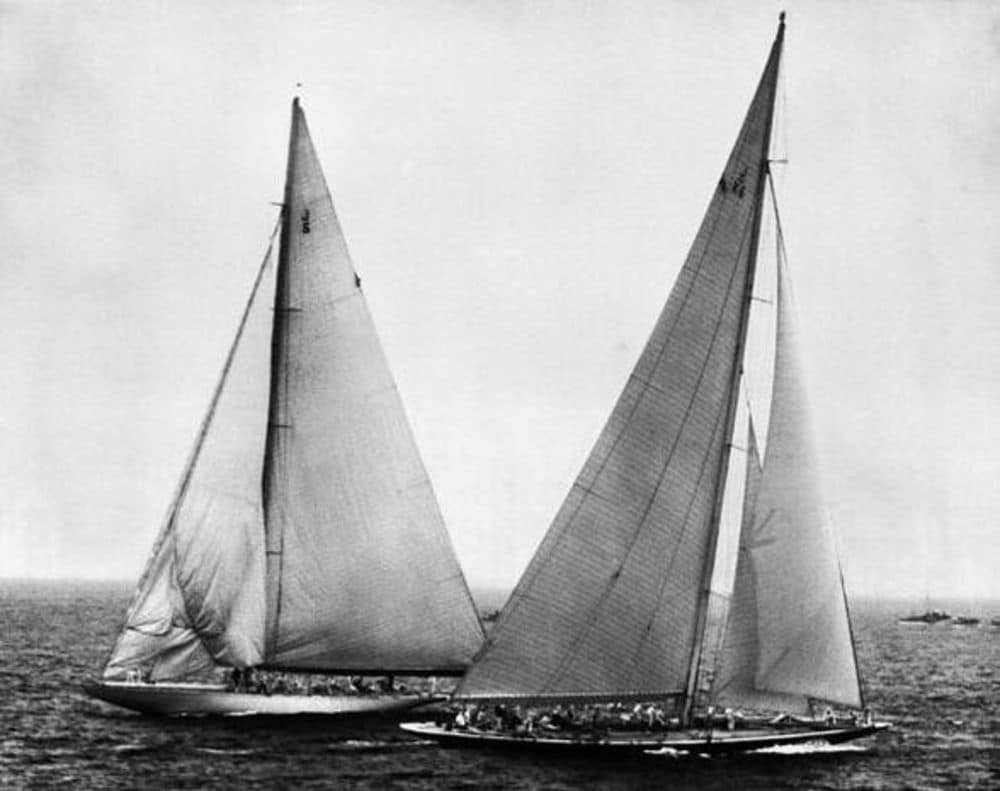

Lipton’s final America’s Cup challenge would come in 1929 in the J-Class. Shamrock V was heavy and outdated compared to Enterprise, which had little trouble in defeating the challenge. In 1934, having purchased Shamrock with the intent of challenging the cup, Sir Thomas Sopwith constructed Endeavor, and subsequently Endeavor II (right) for the challenge, but it was no match for Ranger (left).
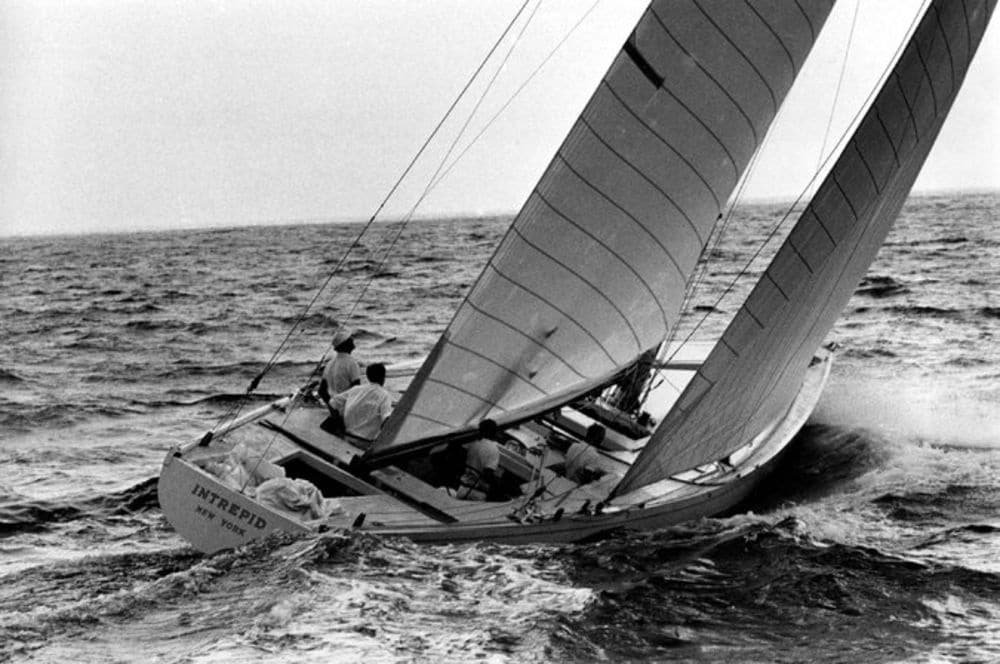

Following the second World War, the 12 Meter rule aimed to reduce the costs and ensure racing could continue in a post-war economy. The first unsuccessful challenge came in 1958, 20 years since the previous attempt by Endeavor II in the J-Class, with Columbia defeating the British challenger Sceptre. Over the next 20 years, the US would defend 7 more challenges, including the first Australian entry in 1962. Intrepid (pictured) would become just the second yacht in history to successfully defend the Cup twice, first in 1967, and again in 1970.
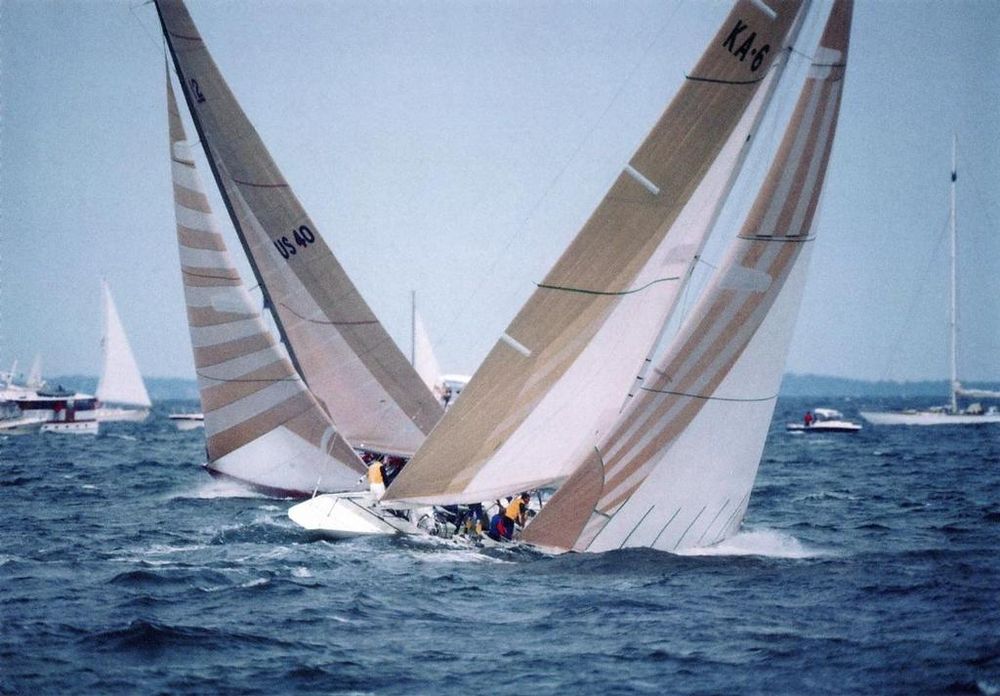

1983 would prove to be a historic and game-changing year for the history of the America’s Cup. Alan Bond, who had made three attempts already at bringing the cup to Australia, returned for a fourth attempt. The design of Australia II‘s (right) keel was kept secret, and in the end, the infamous winged design would prove effective. Australia II overtook Liberty, despite initial problems, and went on to upend the longest winning streak in the history of sports – 132 years.
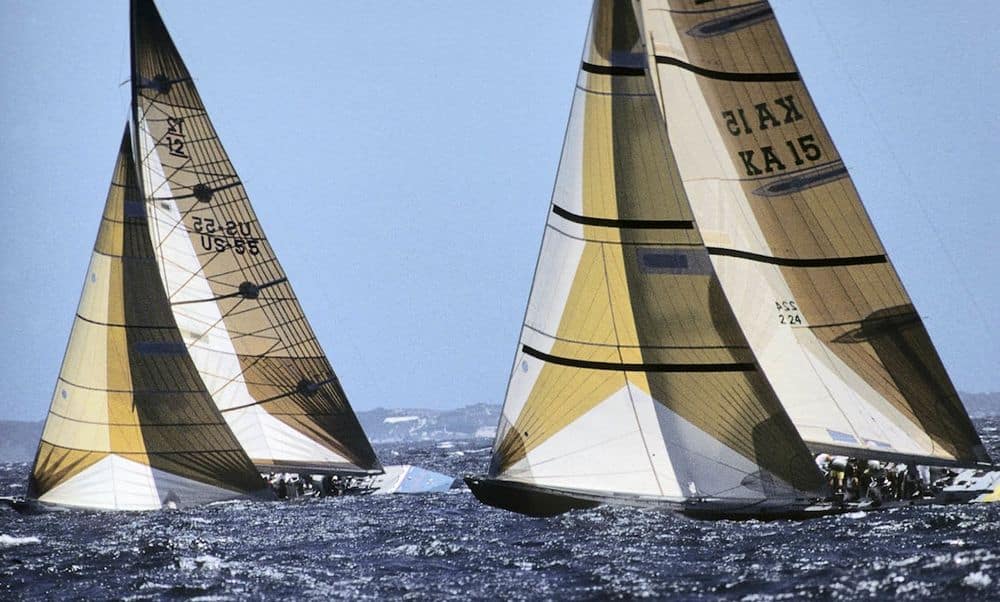

The first Cup defended outside of the United States was held in Fremantle Australia in 1987. From an unexpected field of 13 challengers, American Dennis Conner won the right to challenge the Australians through victory in the Louis Vuitton Cup. Conner easily sailed Stars & Stripes 87 to victory, beating Kookaburra III four races to zero, winning the cup back for the Americans.
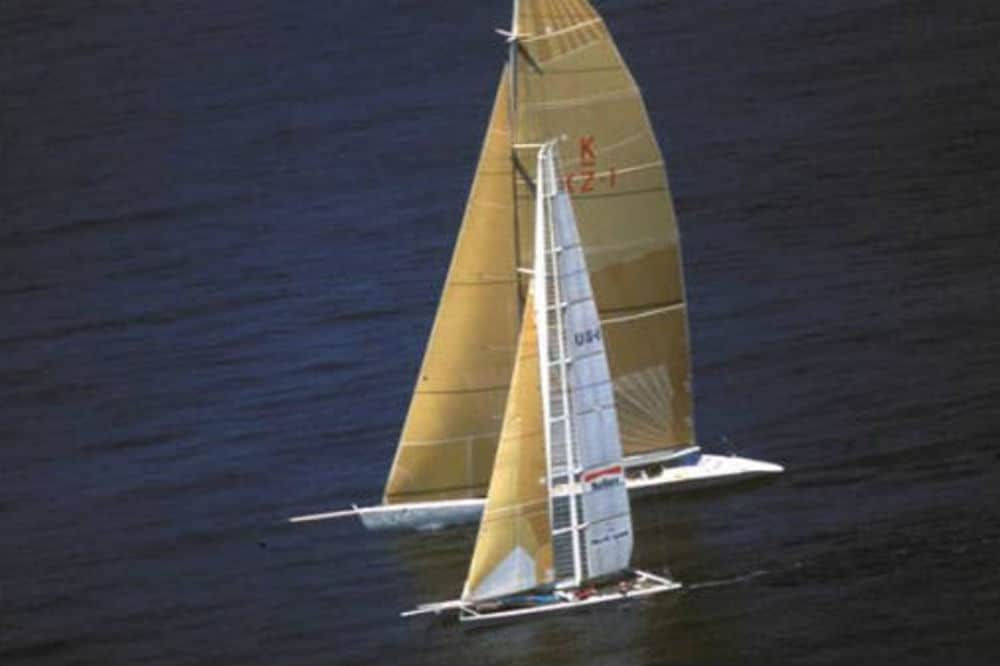

In 1988, an unexpected challenge came from a New Zealand syndicate, which proved to bring about major design changes and controversy never before seen in the America’s Cup. Conner, representing San Diego Yacht Club commissioned a catamaran to respond to the Kiwi challenge, realizing that multihulls were not expressly prohibited by the Deed of Gift. New Zealand’s “Big Boat” design, while cutting edge was inherently disadvantaged against Conner’s catamaran and lost by a significant margin.
After the race, controversy over the legality of the design in the Deed of Gift, and whether or not the spirit of “friendly competition” had been violated was rampant. Challenger Michael Fay took San Diego Yacht Club to court over the matter and was awarded the trophy in the ruling. The decision, however, was overruled and the cup was returned to the Americans.
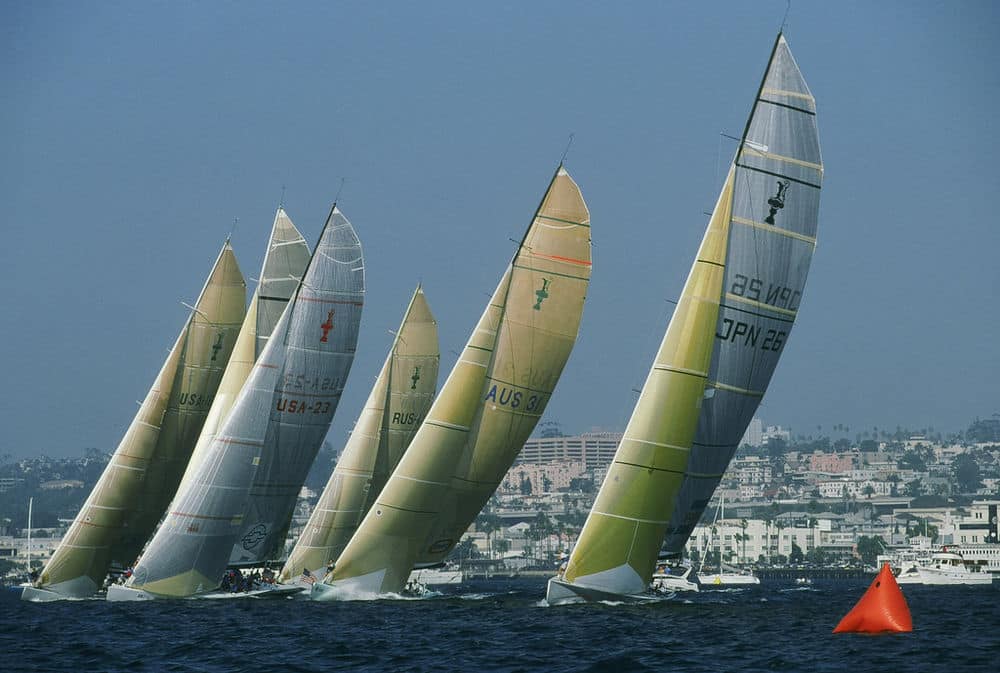

After the controversial 1988 Cup, a new design rule was put in place, and the International America’s Cup Class was born. From 1992 to 2007, the Cup changed hands regularly, with strong teams fielded by Italy, New Zealand and Australia. In the 1995 Cup in San Diego (pictured), New Zealand, skippered by Russel Coutts, scored their first victory, defeating Dennis Conner 5-0.
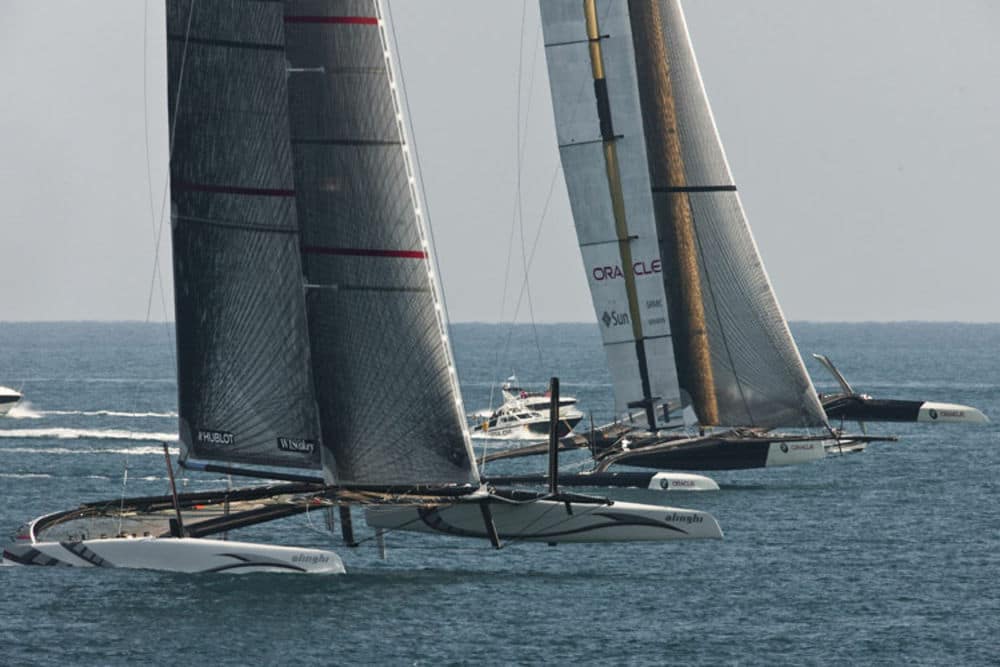

2010 brought more significant design changes to the cup, with BMW Oracle Racing challenging Alinghi in a battle of massive multihulls. BMW Oracle chose a trimaran with a rigid wing sail, similar to the sail used by Conner in the 1988 cup, while Alinghi chose traditional sails for their catamaran. The rigid wing proved to give BMW a significant advantage, and the Cup once again returned to the US.
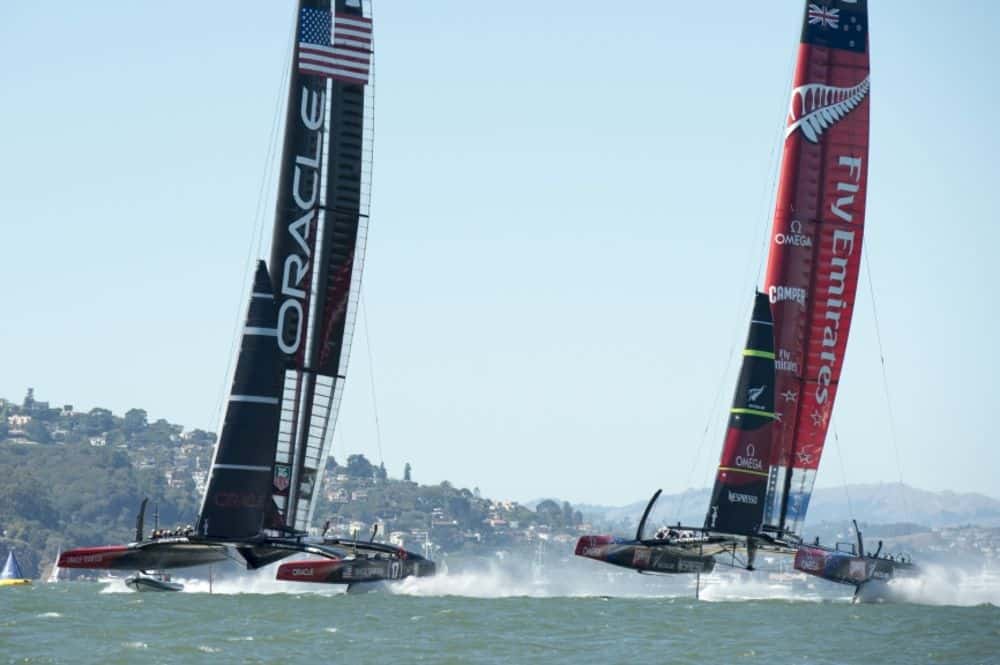

The 34th America’s Cup in 2013 brought about more changes to the America’s Cup class, with the defender, Oracle Team USA opting for the use of 72 foot catamarans for the racing on San Francisco Bay. The catamarans proved again to be a point of controversy over costs limiting the ability of teams to pose challenges, and the risk associated with the new, faster and more dangerous boats. Twice during training, major accidents occurred, and new safety regulations were put in place to ensure the safety of athletes.
Emirates Team New Zealand won the right to challenge Oracle in the finals, after defeating Artemis Racing and Luna Rossa in the Louis Vuitton Cup. In the final, New Zealand started strong, taking a commanding 8-1 lead, but the constant changes to crew and modifications to the boat allowed Oracle Team USA to fine tune their performance and turn the tide in their favor. In an epic comeback, Oracle overturned their 7 win deficit to beat Emirates Team New Zealand and secure the cup for America one again.
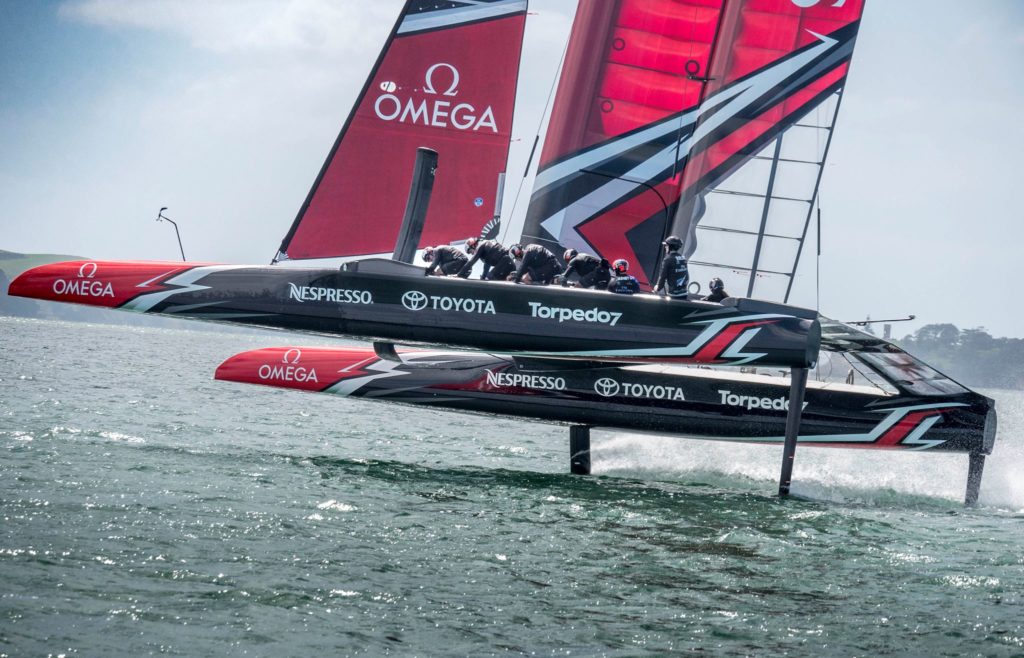

For the 35th America’s Cup in Bermuda, teams agreed to cut costs and improve safety and accessibility by reducing the size of the boats to just 50 feet. Training vessels were allowed, and the AC45F, a smaller, lighter foiling catamaran was selected as the platform for the America’s Cup World Series during 2016-2017. Teams have now launched their final race boats and training has begun for the start of the qualifier series.
In July, 5 teams will meet in Bermuda to battle for the right to challenge Oracle Team USA and determine the fate of the cup until the next challenge.