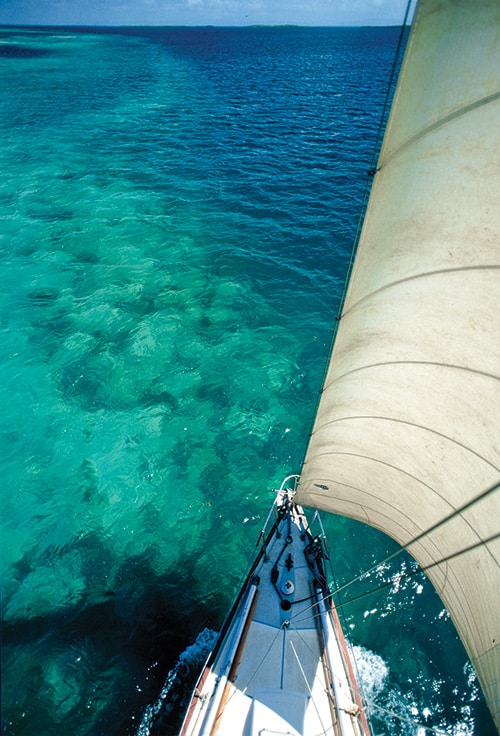
With the almost universal use of GPS and chart plotters, eyeball navigation has largely been forgotten, and in some cases, the result has been disastrous. One can argue endlessly over paper versus e-charts, but one thing’s certain: Over-reliance on electronic navigation supports the local salvagers. Note the case of a Swan 90 hard aground on the western side of Antigua’s Spithead Channel. The grounding occurred because the skipper was looking at his chart plotter rather than using eyeball navigation. The salvage and repair costs ended up in the $800,000 ballpark. If you use common sense — not heading west to enter harbors after 1500 or heading east in reef-encumbered areas before 1100 — you can cruise the Caribbean relying completely on eyeball navigation, as is proved by two stories, one from the late 1950s, the other from the early 1960s.
Marv Berning and Bill Bailey, both in their very early 20s, were crewing on Le Voyageur (now Mariette), a 131-foot Herreshoff schooner. They saved their money, left the boat and bought a 20-foot Bequia double-ender. They installed a deck with a big hatch so they had sleeping accommodations out of the spray and rain, then took off, spending two months cruising from Bequia to St. Thomas, in the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Their navigational equipment consisted of an Esso road map that showed all the islands and a dry Boy Scout compass. To keep the compass level so it would work, they glued it to a piece of wood that they floated in a half-filled gourd whose top had been cut off. They chocked the gourd so it did not fall over; the compass needle gave them north, and they estimated the other compass points. (Note: This was in the days when all sailors had to learn to box the compass, reading off the 32 points and the quarter points!)
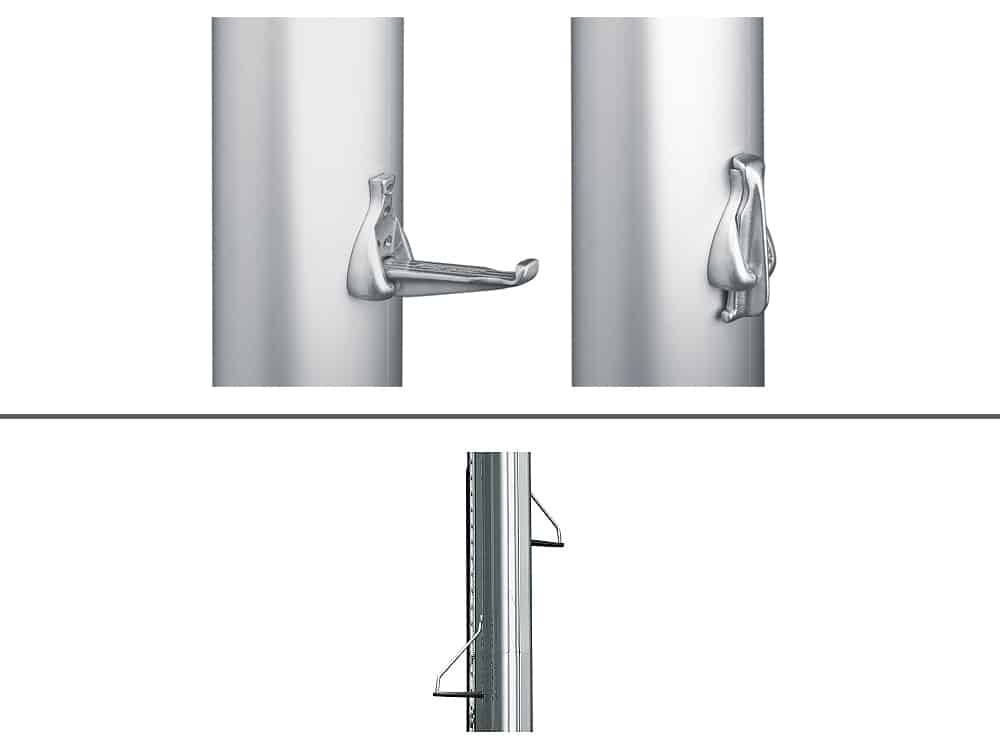

In the early ’60s, my yawl Iolaire departed Grenada on a one-month sail to St. Thomas. The trip was a charter, and on board was a group of six young doctors doing their medical residency at Bellevue Hospital in New York. As we reached the northwest corner of Grenada, I discovered that, because of crossed wires, our charts of the Grenadines had been left in the Grenada Yacht Club bar. Neither I, nor my 18-year-old crewmember, Ed Pionkowski, had ever sailed the Grenadines. The only guide available was my Norie and Wilson Sailing Directions for the West Indies, published in 1867. It was an excellent guide, but for the Grenadines it gave no information other than that one should hire a local pilot.
I was not willing to go back to St. George’s to pick up the charts. Instead, I told Ed to take two small cockpit cushions to the lower spreaders and secure one on each so someone on either spreader would have a comfortable seat. We had a flag halyard on the starboard spreader and rigged another on the port spreader so that no matter which tack we were on, the person on the spreader could be supplied with cold Heineken.
In my early days of chartering and exploring the eastern Caribbean, often without the aid of a detailed chart, one of my crew or I would spend a lot of time conning Iolaire from a perch up the mast.
We spent a week cruising the Grenadines and later entered the Tobago Cays from the southern entrance, a pass that today the bareboat charter managers and guide authors claim is too difficult to use. We found that if there is good light and the skipper reads carefully the sailing instructions on the back of Imray Iolaire chart B31 or B311, or the piloting directions found in Street’s Cruising Guide to the Eastern Caribbean: Martinique to Trinidad, and uses eyeball navigation with a crewmember on the foredeck or up the mast, the southern entrance is not that difficult. Eyeball navigation is much better from the bow than from the cockpit, and standing on top of the bow pulpit is better still than standing on deck. If it is a tight situation or the light is fading, a crewmember piloting from the lower spreaders makes everything clear. In my early days of chartering and exploring the eastern Caribbean, often without the aid of a detailed chart, one of my crew or I would spend a lot of time conning Iolaire from a perch up the mast. Before the late 1970s, when Imray Iolaire charts became available in the marine hardware stores throughout the eastern Caribbean, obtaining charts in the islands was extremely difficult. We ordered ours from the United States or England, and it often took six weeks for them to arrive.
When I first bought Iolaire in 1957, she had a wooden mast with external halyards, thus it was no problem to climb aloft. But over time, rig problems eventually got to me. In 1962 we lost the mast in Anegada Passage. To salvage it, we towed the spar in to Norman Island — at that time, Iolaire had a very small engine that sometimes ran — and hoisted it on deck; powered back to St. Thomas; shortened and scarfed the spar; and were out on charter 11 days later.
Then, in 1966, we lost the top 10 feet of the mast off Dominica. The engine did not run, so we came up with a jury rig and sailed back to Grenada. We averaged 5.5 knots with me, daughter Dory, 7, and a young Grenadian crew aboard.
I decided finally I’d had enough of wooden spars that had to be regularly varnished and whose glue joints let go with disastrous consequences, so I installed an aluminum mast. Even so, I maintained the external halyards, and until I reached my mid-70s, I could still climb Iolaire’s mast without the aid of a bosun’s chair.

As my red beard started going gray and sailors began to ask how old I was, I would reply, “As long as my wife looks young enough to be my daughter and I can climb to the spreaders without the aid of a bosun’s chair, I am 38 and holding!” However, when we moved Iolaire to Europe and I started sailing about the Caribbean aboard Lil’ Iolaire, a 28-foot yawl that had an aluminum mast with internal halyards, I learned that climbing such a spar is only for the young and very fit. Once I realized it was almost impossible for me to climb to the spreaders, I immediately installed mast steps. Despite being over 70, I regularly went up the rig when entering harbors and exploring. In fact, the view from the lower spreaders is great!
Given that nearly all boats now have internal halyards, anyone headed for the Caribbean should check the various catalogs, find steps that are appealing and install them at least to the lower spreaders. Rigging steps is a job that can be done by ship’s crew with the mast in the boat.
Whenever there is a tricky pilotage situation, if someone is on the lower spreaders, everything becomes crystal clear. Also, at anchor, crew who are too nervous to go aloft under sail can climb the mast via the steps and obtain wonderful views and photographs that are not visible from deck level.