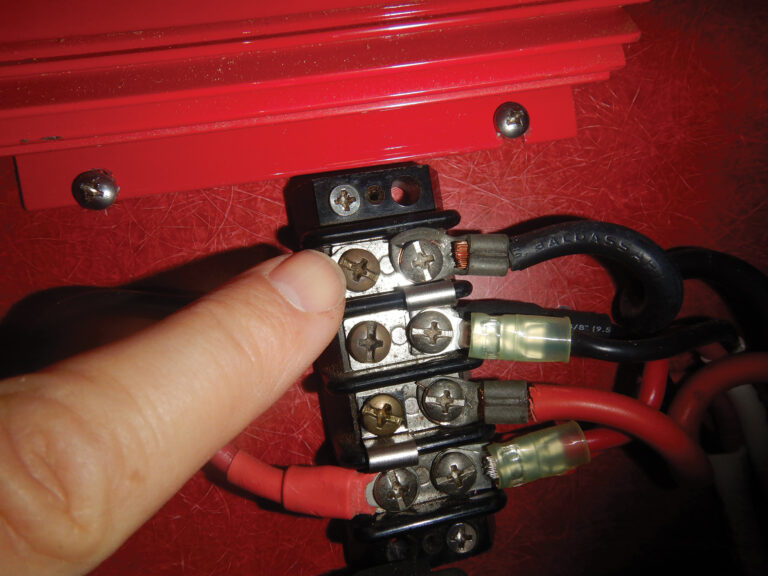
backstay setup
A running backstay is a removable stay that provides aft support to the mast from either the masthead or the point at which an inner forestay is attached. It originated as a response to the material limits of the period. At that time, solid wooden masts, for example, were either too weak or too heavy to be made particularly tall. Therefore, to achieve an acceptable area of sail for the heavy-displacement boats of the day, either the boom had to be extended beyond the transom or a gaff had to be added to the top of the sail—or both. This precluded the use of fixed backstays because the boom and gaffs had to be free to swing across the vessel when it tacked and jibed. As a tack or jibe was initiated, the burdened backstay had to be released and, as the spars swung through, the new, now windward, stay had to be fastened quickly before the entire rig came tumbling down.
With the advent of hollow masts, first of wood and then of alloy, and stainless-steel wire, the aspect ratio of the rigs began to extend to 3-to-1 and beyond. This allowed for the development of the Bermuda or Marconi rig, which eliminated gaffs and shortened the booms considerably without the loss of sail area or performance.
Running backstays, or runners, were then generally found only on cutter-rigged vessels. But through the 1960s and 1970s, the sloop became the rig du jour, and running backstays fell from favor. With the introduction of Freedom Yachts’ freestanding mast and Hunter’s B&R rig, the trend veered toward eliminating backstays, running or not, altogether.
Where are we today? Are running backstays now simply anachronisms that add unnecessary weight, windage, and clutter? I think not, especially in the context of bluewater cruising.
Sloops are fast around the buoys, but in the open sea, they display two disadvantages. First, the sail area is shared by only two large and therefore more difficult to handle sails. Second, in storm conditions, a sloop’s headsail, no matter how much it’s furled, still leaves the center of effort too far forward and too high to produce a safe and comfortable motion.
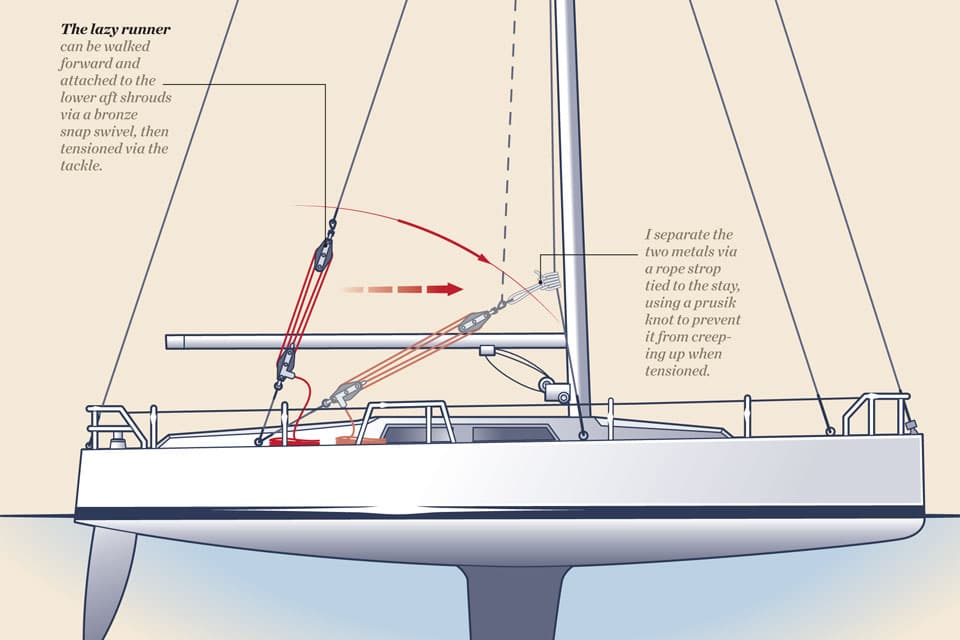
The cutter rig distributes the sail area over an additional sail, and that inner forestay is a superior position from which to hank on a low-flown storm sail. But with any real force upon it, the inner forestay can distort the shape of the mast; this will require a countereffort. Enter the intermediate running backstay. The arguable benefit of a staysail aside, this lower triangulation of support adds strength and stability to the mast, which translates into a better chance of coming up from a knockdown with the rig intact. Think sailing in the South Atlantic Ocean—it matters.
But alas, when you’re sailing off the wind, these same runners will have to be attended to on each and every tack. In open-ocean situations, this might not happen for days at a time. In confined waters, however, it’s necessary to have a quick and efficient method for setting and stowing runners.
Ideas and hardened opinions on running backstays are diverse and plentiful enough to keep seaside barstools warm all night. See the accompanying images and diagrams to learn about some of the most common approaches to setup and stowage.
If you’re considering adding an inner forestay and running backstays, I recommend that you get professional advice addressing the minimum engineering angles required, appropriate deck hardware, proper tangs and toggles needed at the mast, and wire types and diameters.
I don’t mean to imply that running backstays are suitable for all boats and applications. But if your interests lie in bluewater passagemaking and you take a belt-and-suspenders approach to your safety, I believe that you’ll agree that the added weight, windage, cost, and inconvenience are more than justified.
Alvah Simon, a CW contributing editor, is the author of North to the Night.
Click here for more pictures of running backstay setups.
Click here to read about how an inner forestay and staysail can help you beat along in a blow.