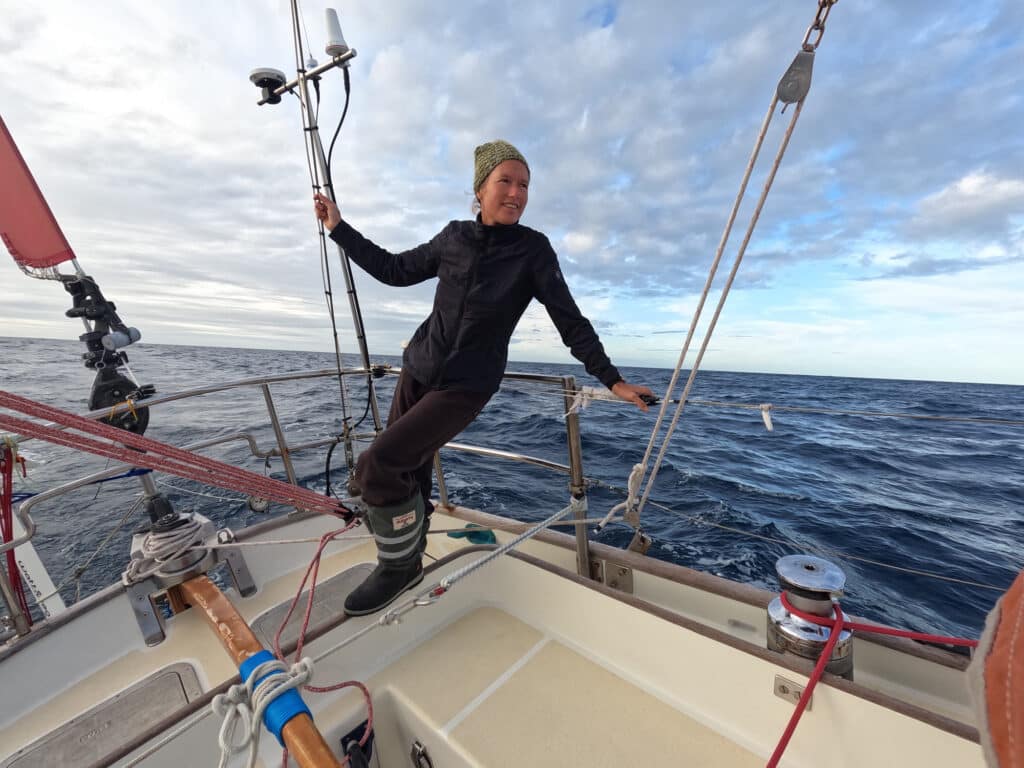
When Kirsten Neuschäfer decided to compete in the 2022-23 Golden Globe Race, she searched for a fast, safe and stable boat. She studied designs with a good ballast-to-weight ratio, and sought out a hull and rig that could withstand a hard beat to windward.
She found Minnehaha in Newfoundland and knew that the tough, sturdy Cape George 36 was the one. The quick cutter with a generous sail plan met all of the official requirements—a production boat with a full keel, less than 36 feet long, designed before 1988—and a few requirements she had set for herself.
“I wanted a super-secure boat for the Southern Ocean, which was fast as well,” Neuschäfer says. “Minnehaha suffers a little in light airs, but I knew I had a good chance of surviving. It was clear to me that the GGR was a bit of a race of attrition.”
Her instincts, along with detailed preparation, hard work and a bit of luck, served her well. Eight months after 16 skippers set out from the west coast of France to race solo 30,000 miles eastbound around a Southern Ocean course, Neuschäfer and Minnehaha caught one last whisper of wind off Les Sables d’Olonne, ghosted over the line, and sailed into history.
“I didn’t actually know that I’d won until the boats came out to meet me,” the South African sailor said of her historic finish. “I knew I was very close to Abhilash, so I was pushing hard. I knew we were very close.”
Indian skipper Abhilash Tomy battled the same light airs that Neuschäfer faced near the end of the race and arrived a day after, taking second place. Austrian Michael Guggenberger finished third, as the final skipper to complete the race in the racing class.
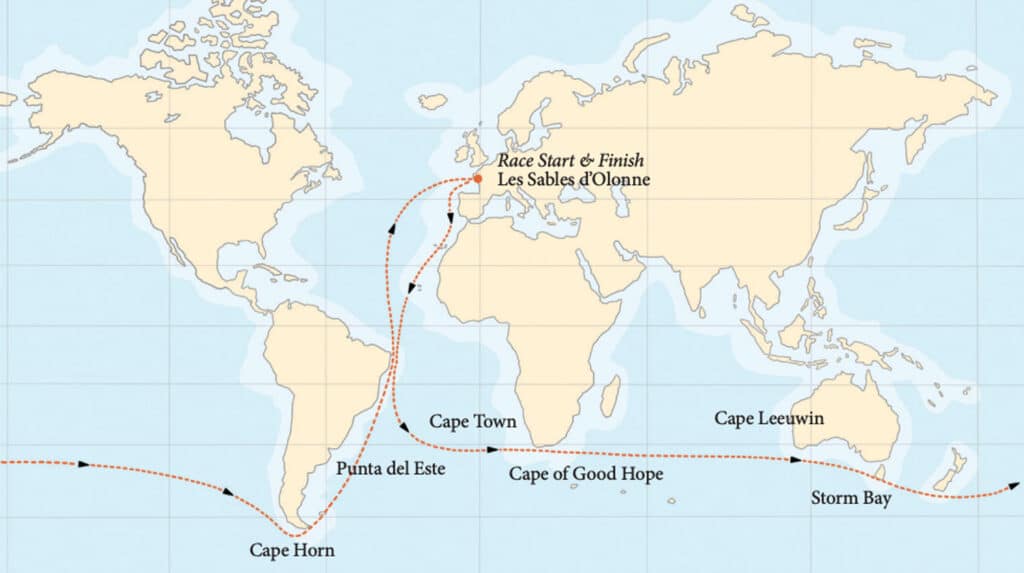
The Golden Globe Race is a nonstop, solo, unassisted round-the-world race with the start and finish line in Les Sables d’Olonne. Competitors are required to sail small boats using paper charts, VHF radio, sextants and celestial navigation. No modern weather-routing software is allowed, nor satellite communication, electronic instruments and autopilots.

The route takes the sailors south through the Atlantic before heading east to Cape Town, South Africa, and around the Cape of Good Hope. After crossing the Indian Ocean and keeping Tasmania to port, sailors traverse the storm-plagued Southern Ocean and round Cape Horn. The final stretch leads north through the Atlantic and back to Les Sables d’Olonne.
Of the 16 skippers who started the 2022-23 race, 11 retired and two others made a single stop, moving them out of competition and into the Chichester Class. Neuschäfer’s victory made her one of only three people to win the race—and the first woman ever to win a solo circumnavigation yacht race.
“Minnehaha suffers in light airs, but I knew I had a good chance of surviving. The GGR is a race of attrition.”
The race is based on the 1968-69 Sunday Times Golden Globe Race, won by Sir Robin Knox-Johnston aboard his 32-foot Bermudan ketch, Suhaili. Knox-Johnston was the only skipper to finish; in doing so, he became the first person to solo-circumnavigate the globe nonstop. Nine others retired, one was dismasted, and one committed suicide. The race was run once more in 2018, on the 50th anniversary of the original race. Eighteen sailors set out, and five finished. French sailor Jean-Luc Van Den Heede won the 2018 edition.
More people have gone into space than have sailed singlehanded around the world. The small nature of the club means that the sailors, while competing, still look out for one another’s health and safety.
During the first dash south down the Atlantic in the 2022-23 race, Neuschäfer relayed to the race committee the VHF-radio mayday call of fellow sailor Guy DeBoer, who’d hit rocks near the Canary Islands. After a night spent grinding over the rocks, DeBoer abandoned his boat the next morning with the help of a local rescue team.
Two months later, 450 miles southeast of Port Elizabeth, South Africa, Tapio Lehtinen’s Gaia 36, Asteria, flooded after taking on water from astern, and sank in less than 20 minutes. Lehtinen had just enough time to activate his EPIRB, put on his survival suit, and swim to his drifting life raft. “I gave Asteria a last standing salute as she went down,” the Finnish skipper said. Neuschäfer, the closet sailor to his position, altered course and hand-steered through the night to assist in his rescue.
“The emergency handheld GPS showed Tapio’s coordinates,” Neuschäfer says. “I followed the track, but it was very difficult to spot a small, orange life raft. I was able to reach him on the VHF, but the early morning light was behind him, and I couldn’t see him. He fired off a flare, and I approached him on a beam reach. He’d been waiting 24 hours and was ready. He threw me a line, and I caught it on the first try, pulled him in, tied the life raft to Minnehaha, and helped him aboard.”
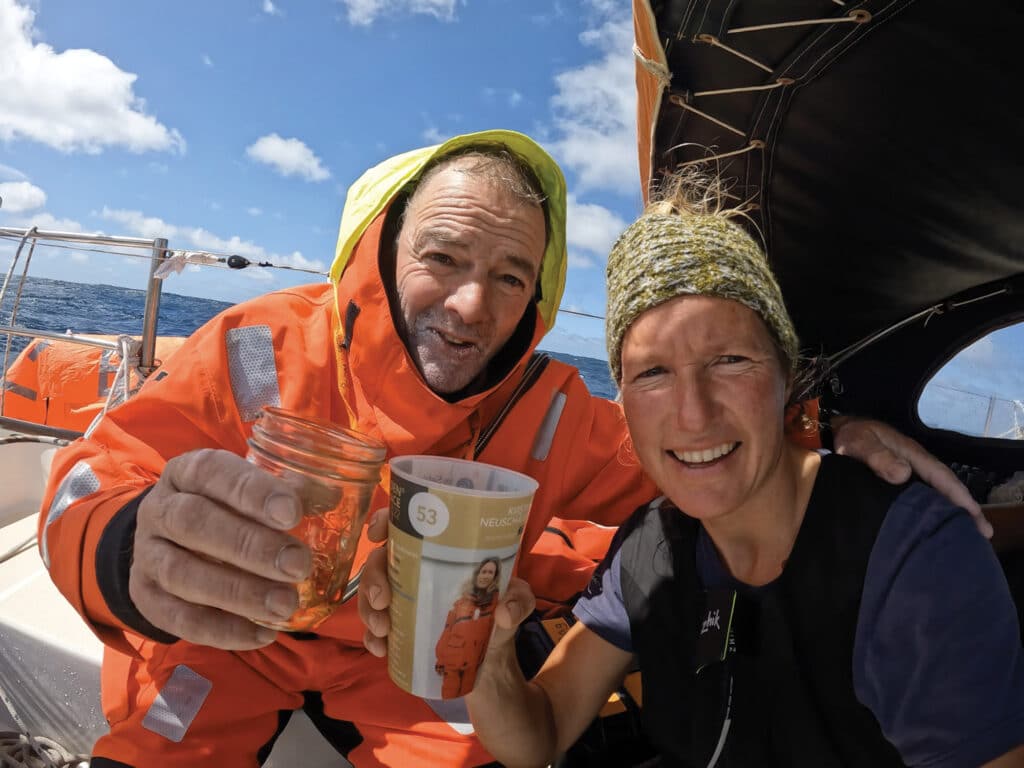

The two sailors shared a glass of rum. An hour later, Neuschäfer managed Lehtinen’s dangerous transfer from Minnehaha to bulk carrier Darya Gayatri, a freighter that had responded to the emergency call as well. “When I saw he was on board, I was just relieved for him,” she says.
Neuschäfer’s own heavy-weather plan focused on mitigating risks and staying true to strategies she’d set. When a low-pressure system approached on her way south to Cape Horn, she set a warp off her stern and held on for 12 hours until the storm blew over. In strong winds north of the Falklands, she hove-to, knowing that beating to windward in the extreme conditions risked damage to her boat.
By this time in her life, she was no stranger to adventure. Neuschäfer’s early years had led her from South Africa to a set of jobs in Europe, followed by a solo trans-Africa biking trip, where she pedaled the continent north to south in her 20s. Her later experience working for Skip Novak on his Pelagic Expeditions exposed her to the wind and weather systems of the Antarctic Peninsula, Patagonia and the Falklands, and built her familiarity with the Southern Ocean.

“You need a great deal of self-sufficiency on these expeditions,” she says. “You need to know which tools and spares to bring. You need to be able to do all kinds of troubleshooting, refit the boats, change out a propeller, or fix a rig under difficult weather conditions.”
Neuschäfer had also done several long-distance deliveries, including taking a Leopard catamaran from the South Africa factory to Australia, and completing a singlehanded delivery from Portugal to South Africa on what she calls a labor-intensive boat. “This, that and the next thing needed to be done, and I discovered that I can solve problems out at sea,” she says.
As she followed the 2018 Golden Globe Race, she liked its spirit of adventure. “There are a lot of reasons to decide not to do something,” she says. “Having succeeded and followed my heart in other decisions, I knew that the GGR was something I should do.”
Her plans were nearly derailed early when she left her boat in Newfoundland and flew to South Africa, and then COVID-19 restrictions kept her from returning to Canada. She was eventually able to get back to Newfoundland and sail to Prince Edward Island, where she spent a year preparing for the race. She fell in love with the people there and made lifelong friends. Several were present at the Golden Globe Race finish line in Les Sables d’Olonne.

For her part, Neuschäfer makes light of the fact that the race dubbed a “Voyage for Madmen” was won by a woman. “I entered as a sailor,” she says. “I competed as a sailor and won as a sailor. On the same token, it’s a male-dominated race. If what I did inspires someone, then good will come of it, and I’m happy for that.”
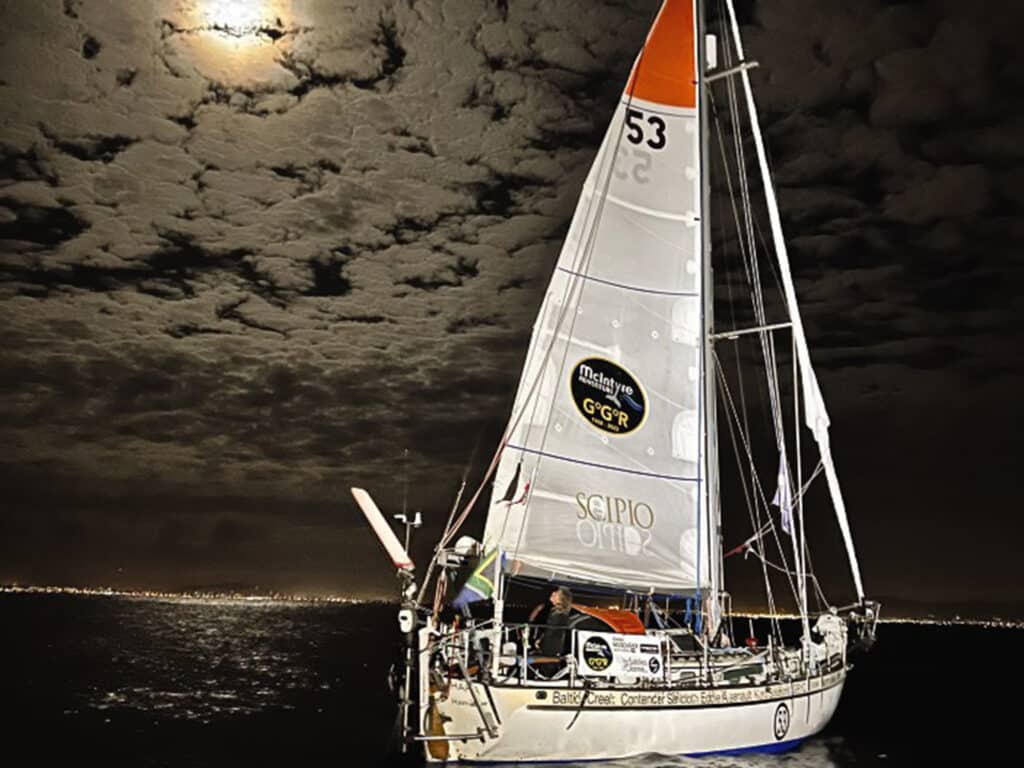
Neuschäfer clearly has inspired the sailing world. On the final night of her race, as Minnehaha made its way up Les Sables d’Olonne channel, thousands of supporters lined the harbor walls, cheering and waving flares. Neuschäfer’s smile lit up the night. When she reached the dock, a friend handed her a bottle of champagne, which she sprayed into the air. Dressed in her sailing bibs and bare feet, she stepped off her boat and onto dry land for the first time in 235 days, and hugged her mother.
Theresa Nicholson is CW’s senior editor.